Introduction to Arginine
Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including protein synthesis, immune response, and the production of important molecules such as nitric oxide. In its natural form, arginine is involved in several physiological processes, especially those linked to vascular health and muscle growth. However, the inclusion of the name “O’Connor” in “Arginine OConnor” may refer to a person or a creative concept, blending the biochemical importance of arginine with cultural or individual significance. This article will focus primarily on L-arginine, its benefits, uses, and how it is integral to various health systems, from cardiovascular wellness to sports nutrition.
What Is Arginine?
Arginine is one of the 20 amino acids that the body uses to create proteins. Unlike essential amino acids, which must be obtained from food, arginine is classified as “semi-essential” because the body can usually produce it from other amino acids when needed. Under certain conditions, however, such as during illness or stress, the body’s demand for arginine exceeds its production, making supplementation necessary. This is why arginine is often considered both a naturally occurring substance and one that can be obtained from external sources.
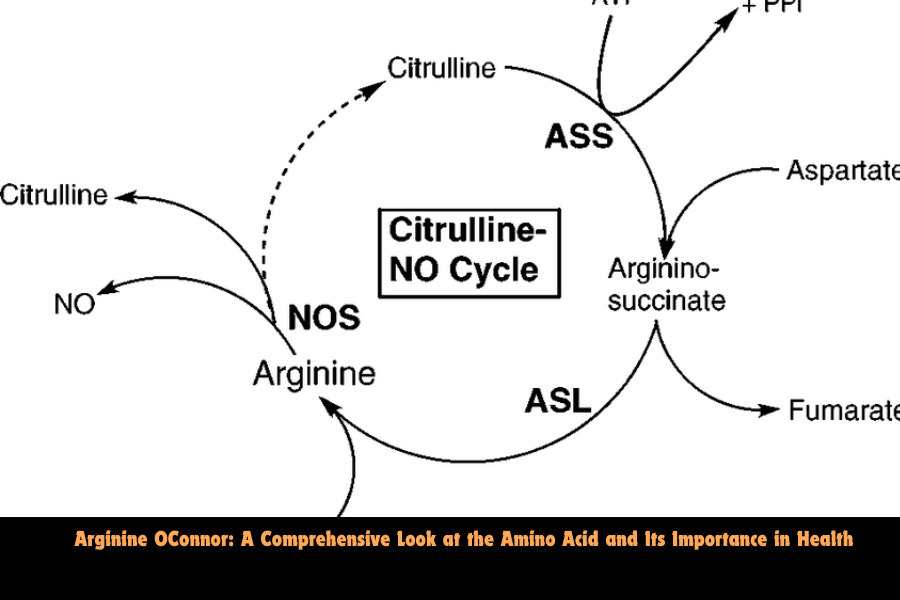
Arginine is most commonly recognized for its ability to convert into nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide is a vital compound that helps blood vessels relax and widen, improving blood flow and nutrient delivery throughout the body. This is particularly significant for cardiovascular health and is why arginine supplements are frequently used in heart disease prevention.
Wiki
| Attribute | Details |
| Chemical Name | L-Arginine |
| Synonyms | 2-Amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid, L-Arg, L-Arginine HCl |
| Molecular Formula | C₆H₁₄N₄O₂ |
| IUPAC Name | (S)-2-Amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid |
| CAS Number | 74-79-3 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.2 g/mol |
| Function in the Body | Precursor to nitric oxide, protein synthesis, supports cardiovascular health, immune function |
| Sources | Meat (turkey, chicken), dairy, nuts (almonds, peanuts), legumes (lentils, chickpeas), pumpkin seeds |
| Common Uses | Treating erectile dysfunction, supporting muscle growth, reducing blood pressure, improving circulation |
| Supplements | Available as L-Arginine powder, capsules, tablets, and in combination with other amino acids |
| Recommended Daily Intake | 2–3 grams per day (for general health), higher for specific conditions (up to 6 grams or more) |
| Side Effects | Diarrhea, nausea, stomach pain, potential low blood pressure |
| Precautions | Consult a healthcare provider if you have cardiovascular issues, low blood pressure, or taking medication |
| Potential Benefits | Increased nitric oxide levels, improved athletic performance, better recovery post-exercise |
The Role of Arginine in the Body
Arginine’s most well-known function is in the production of nitric oxide, which impacts several key physiological systems.
Nitric Oxide Production
Arginine is a precursor to nitric oxide, a molecule that plays a pivotal role in dilating blood vessels, improving circulation, and regulating blood pressure. Nitric oxide helps relax the endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels), allowing them to expand and improve blood flow. This is crucial for cardiovascular health, as it helps reduce the risk of heart disease, lowers blood pressure, and supports proper endothelial function.
Protein Synthesis and Muscle Health
As an amino acid, arginine is essential for protein synthesis. It aids in muscle repair and growth, making it a staple supplement in bodybuilding and athletic circles. It helps transport nitrogen to muscles, ensuring that the body remains in a positive nitrogen balance—an essential state for muscle growth and recovery after intense exercise. Arginine is also linked to enhancing muscle endurance, as better blood flow increases oxygen and nutrient delivery to muscles.
Immune System Support
Arginine supports immune health by promoting the production and function of white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting infections. It also helps regulate the production of cytokines, molecules that mediate immune responses. During periods of illness or stress, arginine supplementation may support the body’s increased demand for immune function.
Wound Healing
Arginine is involved in collagen synthesis and tissue repair, making it a valuable nutrient for wound healing. When the body undergoes physical trauma or surgery, it requires more arginine to repair damaged tissues and promote faster recovery. This is why arginine supplements are sometimes recommended for post-surgery recovery or to manage chronic wounds.
Benefits of L-Arginine
Cardiovascular Health
The benefits of arginine are most prominently seen in cardiovascular health. By improving blood flow, arginine can help reduce the risk of heart disease. Studies have shown that it can aid in reducing blood pressure, increasing circulation, and even helping people with erectile dysfunction due to improved vascular health. Arginine’s ability to boost nitric oxide production is central to these benefits. Additionally, arginine has been linked to improved endothelial function, which is crucial for maintaining the health of blood vessels and arteries.
Athletic Performance
In the world of sports nutrition, arginine is a favorite among athletes for its performance-enhancing properties. It has been shown to improve endurance by enhancing blood flow, which allows for better oxygen delivery to muscles during physical activity. This can delay the onset of fatigue and enhance recovery post-exercise. It also has muscle-boosting effects, which is why it is often included in pre-workout supplements.
Erectile Dysfunction
One of the more popular uses of arginine in the health space is for treating erectile dysfunction (ED). ED is often caused by poor blood circulation, and since arginine promotes blood vessel dilation, it can help improve blood flow to the penis. Some studies suggest that taking arginine supplements can help manage symptoms of ED, especially in combination with other treatments such as pycnogenol (a form of pine bark extract). However, it’s important to note that its effectiveness can vary, and it may not be suitable for all individuals.
Blood Pressure Regulation
Arginine is often used to manage high blood pressure, particularly in people with hypertension. By promoting the production of nitric oxide, arginine helps relax blood vessels, which can lead to lower blood pressure levels. For those already on medication for high blood pressure, it’s important to monitor interactions, as arginine can intensify the effects of blood pressure-lowering drugs.
Dietary Sources of Arginine
While the body can synthesize arginine, certain circumstances—such as illness, stress, or intense physical activity—may increase the need for supplementation. There are many dietary sources of arginine, particularly for individuals who prefer to meet their needs through food rather than supplements.
Animal-based sources:
Meat: Red meat, poultry, and fish are rich sources of arginine. Turkey, in particular, contains high amounts of arginine.
Dairy: Milk, yogurt, and cheese can provide moderate levels of arginine.
Plant-based sources:
Nuts and seeds: Pumpkin seeds, peanuts, and almonds are excellent plant-based sources of arginine.
Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and soybeans also contain arginine.
Whole grains: Quinoa and oats are other good sources.
In addition to these foods, arginine is also available in supplement form as powders, capsules, and even in some energy drinks and protein shakes designed for athletes.
Arginine Supplements and Their Uses
For those who cannot meet their arginine needs through diet alone, supplements provide an efficient option. The typical dosage for L-arginine supplementation ranges from 1.5 to 24 grams per day, depending on the individual’s health goals and needs.
Pre-Workout Supplements
Arginine is frequently found in pre-workout supplements designed to boost energy, endurance, and recovery. By promoting nitric oxide production, it enhances blood flow, which helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to muscles during exercise. This results in improved exercise performance, particularly in high-endurance activities such as running or weightlifting.
Heart Health
For individuals looking to improve heart health, L-arginine supplements are sometimes recommended as part of a broader regimen to help manage conditions like hypertension or atherosclerosis. The supplementation can help maintain proper vascular function, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Recovery and Muscle Growth
Athletes often take arginine to help with post-exercise recovery. By improving blood flow and accelerating the removal of metabolic waste products, such as lactic acid, arginine supplements can help reduce muscle soreness and enhance muscle repair and growth. It can also be combined with other amino acids like citrulline to improve its effects on performance.
Side Effects and Interactions of Arginine
While arginine is generally safe for most people, some may experience side effects, especially when taken in large doses. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and bloating. People with certain pre-existing health conditions or those on medications should exercise caution.
Blood Pressure: Since arginine can lower blood pressure, it may interact with antihypertensive medications, potentially causing blood pressure to drop too low.
Blood Clotting: Arginine may slow blood clotting, so it should be used with caution in people who are taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet medications.
Kidney and Liver Conditions: People with kidney or liver disease should consult their healthcare provider before using arginine supplements, as excessive levels may worsen certain conditions.
Arginine and Its Role in Holistic Health
Arginine plays a key role in a variety of holistic health practices. Whether used for its heart health benefits, its ability to aid in muscle growth, or its impact on recovery and immune function, arginine is an essential amino acid that supports overall well-being. By enhancing blood flow, supporting protein synthesis, and boosting nitric oxide production, arginine supplements offer a wide range of benefits to those seeking better health, improved fitness, and increased vitality.
Conclusion
Arginine is a vital amino acid with multiple health benefits, particularly in enhancing cardiovascular health, improving athletic performance, supporting immune function, and promoting muscle recovery. Its ability to convert into nitric oxide allows it to dilate blood vessels, improving circulation and lowering blood pressure, which makes it a key player in maintaining overall health. Furthermore, arginine is indispensable for athletes, bodybuilders, and those recovering from surgery due to its role in protein synthesis and muscle repair.
While the body can naturally produce arginine, dietary sources like meat, nuts, and legumes, as well as supplements, provide an efficient way to boost its levels when necessary. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting an arginine supplement regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those taking certain medications. Arginine’s versatility makes it a significant component in the fields of health, fitness, and medicine, contributing to both physical wellness and recovery.
FAQs about Arginine OConnor
1. What is Arginine OConnor?
While “Arginine OConnor” may appear to combine the biochemistry term “arginine” with “O’Connor,” it is not a well-known term in scientific literature. It is possible that “O’Connor” refers to an individual or context not directly related to the amino acid itself. This article primarily focuses on the amino acid L-arginine and its importance to human health.
2. What are the main benefits of L-arginine?
L-arginine provides several benefits, including improving blood flow by boosting nitric oxide levels, which helps regulate blood pressure and support cardiovascular health. It also aids in muscle recovery and growth, enhances athletic performance, and supports immune function.
3. Can arginine help with erectile dysfunction?
Yes, arginine is commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction because it promotes blood flow to the penis by increasing nitric oxide production. While it may help some individuals, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
4. Is arginine safe to take as a supplement?
For most people, arginine supplements are generally safe when taken in appropriate doses. However, individuals with conditions like low blood pressure or those taking blood-thinning medications should exercise caution. It’s always best to consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation, especially if you are taking other medications or have health concerns.
5. How can I get more arginine in my diet?
Arginine can be obtained from a variety of foods, including meats (especially turkey), dairy products, nuts (like almonds and peanuts), and legumes (such as lentils and chickpeas). Additionally, certain foods like pumpkin seeds and soy products are great sources of plant-based arginine.
6. What are the side effects of taking too much arginine?
Taking excessive amounts of arginine can cause side effects such as bloating, diarrhea, and stomach discomfort. In some cases, it may lower blood pressure too much, especially if combined with medications. It’s crucial to stick to recommended dosages and consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
7. How does arginine improve athletic performance?
Arginine helps by enhancing blood flow, which ensures that muscles receive more oxygen and nutrients during physical exertion. This leads to improved endurance, reduced fatigue, and faster recovery after exercise, making it a popular supplement in sports nutrition.
8. Can arginine help lower blood pressure?
Yes, arginine has been shown to help lower blood pressure, especially in individuals with hypertension. Its ability to produce nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels and improves blood flow, contributes to this benefit. However, individuals taking blood pressure medication should consult their doctor before using arginine supplements.
Discover the latest news and updates on Magazine Format